Wind energy is a renewable and sustainable power source derived from the kinetic energy of moving air. It has gained prominence as a viable alternative to fossil fuels, contributing to a cleaner environment and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. This article will delve into the principles of wind energy, explore how wind power systems operate, and provide insights into the design and implementation of wind farms.
Table of Contents
- 1. Understanding Wind Energy
- 2. How Wind Power Works
- 3. Components of a Wind Turbine
- 4. How to Design a Wind Farm
- 5. Environmental and Economic Considerations
- 6. Future of Wind Energy
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Understanding Wind Energy
Wind energy is generated by harnessing the natural flow of air currents in the atmosphere. As wind moves, it carries kinetic energy, which can be converted into mechanical energy and subsequently into electrical energy using wind turbines. Wind energy is not only renewable but also abundant and widely distributed, making it a crucial component of global energy strategies aimed at sustainability and reducing carbon footprints.
The amount of energy that can be extracted from the wind is influenced by several factors, including wind speed, air density, and the turbine's design. Wind energy is typically characterized by its capacity factor, which is the ratio of actual output over a period to its potential output if it were to operate at full capacity during the same period.
2. How Wind Power Works
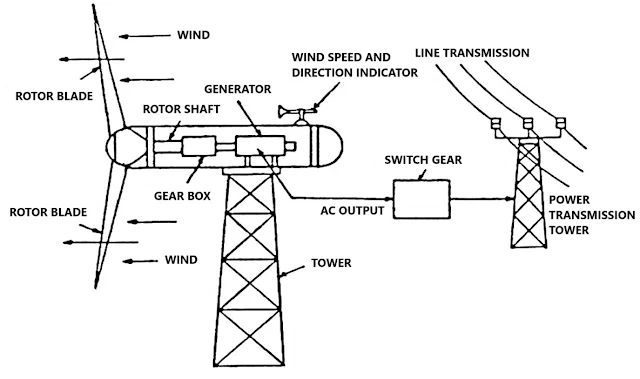
Wind power systems convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity through a series of mechanical processes. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how wind power works:
- Wind Capture: Wind energy begins with the capture of wind by the turbine's blades. As the wind blows, it creates lift, causing the blades to rotate.
- Mechanical Energy Conversion: The rotational motion of the blades is transmitted to a rotor connected to a generator. The rotor is designed to optimize energy extraction based on the wind's speed and direction.
- Electrical Energy Generation: The generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. This process involves moving conductors through a magnetic field to produce electricity.
- Power Transmission: The generated electricity is then transmitted through power lines to substations and eventually to the end users.
Figure 1 illustrates the process of wind energy conversion:
3. Components of a Wind Turbine
Wind turbines are engineered systems composed of several critical components, each playing a vital role in energy conversion:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Blades | Designed to capture wind energy, blades are aerodynamically shaped to maximize lift and minimize drag. |
| Rotor | The rotor consists of the blades and hub; it converts wind energy into rotational energy. |
| Gearbox | The gearbox increases the rotor's rotational speed to match the generator's speed requirements. |
| Generator | The generator converts mechanical energy from the rotor into electrical energy using electromagnetic induction. |
| Tower | The tower supports the turbine and elevates it to capture higher wind speeds, ensuring optimal performance. |
| Control System | The control system manages the turbine's operation, adjusting blade pitch and yaw to optimize energy capture and protect against damage in high winds. |
4. How to Design a Wind Farm
Designing a wind farm involves several critical steps that ensure optimal performance and minimal environmental impact. The following aspects should be considered:
Site Assessment
The first step in wind farm design is conducting a thorough site assessment. This includes evaluating wind resources, land use, and environmental factors. Key considerations are:
- Wind Resource Evaluation: Utilize anemometers to measure wind speeds and directions over time. This data helps identify the most favorable locations for turbine installation.
- Topography: Assess the terrain, as hills, valleys, and obstructions can affect wind flow patterns and energy production.
- Environmental Impact: Conduct environmental assessments to understand the potential impacts on local wildlife, ecosystems, and human communities.
Turbine Selection
Selecting the right turbine is crucial for maximizing energy capture. Factors to consider include:
- Rated Capacity: Choose turbines based on the expected wind conditions and energy generation needs.
- Cut-in and Cut-out Speeds: Ensure the selected turbines can operate efficiently within the expected wind speed range.
- Height and Diameter: Larger turbines can capture more energy but may require more robust structures and increased investment.
Layout Design
The layout of the wind farm is critical to minimizing turbulence and maximizing energy generation. Considerations include:
- Spacing: Turbines should be spaced adequately (typically 5-10 rotor diameters apart) to minimize wake effects from upstream turbines.
- Access Roads: Plan for access roads for construction, maintenance, and emergency response, ensuring they do not disrupt local ecosystems.
- Grid Connection: Design an efficient grid connection to transmit generated electricity to the local power network.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure compliance with local, state, and federal regulations regarding wind farm development. This includes obtaining necessary permits, adhering to safety standards, and addressing any community concerns through public consultations.
Construction and Operation
After planning and permitting, the construction phase begins, followed by the operation of the wind farm. Maintenance plans should be established to ensure long-term performance and reliability.
5. Environmental and Economic Considerations
Wind energy is recognized for its environmental benefits, including:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Wind power generates electricity without emitting CO2, contributing to climate change mitigation.
- Minimal Water Usage: Wind energy systems require little to no water for operation, conserving vital water resources.
- Land Use: Wind farms can coexist with agricultural land, allowing for dual land use and economic benefits for local farmers.
Economically, wind energy creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, contributing to local and national economies. Furthermore, the decreasing costs of wind technology make it a competitive source of energy compared to fossil fuels.
6. Future of Wind Energy
The future of wind energy appears promising as technology continues to advance. Innovations such as larger, more efficient turbines, offshore wind farms, and energy storage solutions are set to enhance the viability and reliability of wind power. Additionally, supportive policies and investments in infrastructure will further facilitate the growth of wind energy as a cornerstone of sustainable energy systems worldwide.
7. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is wind energy?
A: Wind energy is the energy obtained from the wind, which is harnessed using wind turbines to generate electricity.
Q2: How do wind turbines work?
A: Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy through rotating blades, which then powers a generator to produce electricity.
Q3: What factors affect wind energy production?
A: Wind speed, air density, turbine design, and the spacing of turbines in a wind farm significantly influence energy production.
Q4: How is a wind farm designed?
A: Designing a wind farm involves site assessment, turbine selection, layout design, regulatory compliance, and planning for construction and operation.
Q5: What are the environmental benefits of wind energy?
A: Wind energy reduces greenhouse gas emissions, conserves water resources, and allows for sustainable land use.